Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian Cysts What Are They?
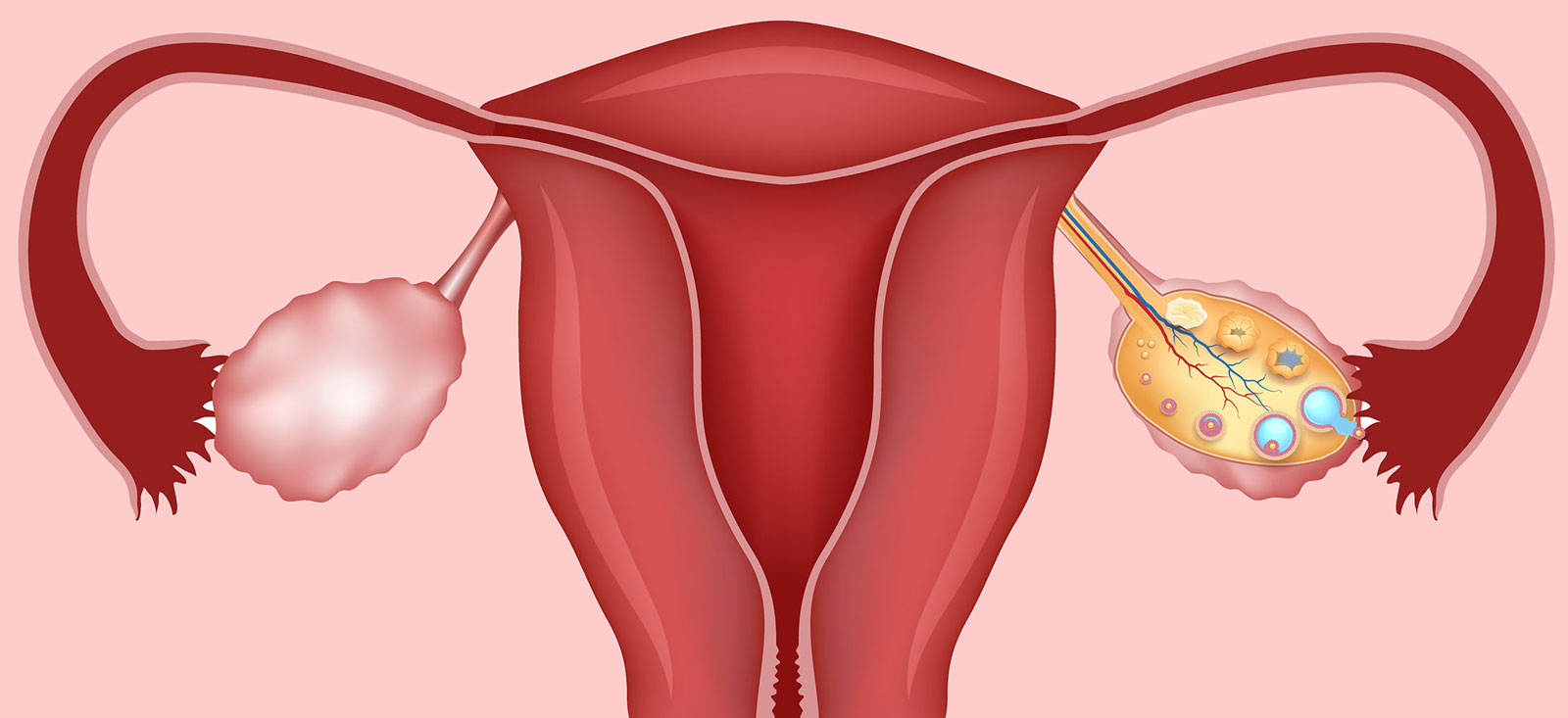
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled or tissue-filled sacs that can develop in the ovaries, which are part of the female reproductive system. These cysts, often forming in most women during each menstrual cycle, are usually harmless and may resolve on their own. However, in some cases, they may require treatment if specific symptoms are present.
Types of Ovarian Cysts
Functional Cysts: Temporary cysts that occur during the menstrual cycle. They are typically benign and can resolve on their own within a few months.
Endometrioma: A type of cyst associated with endometriosis. Endometrioma, resulting from the spreading of the inner uterine lining outside the uterus, can cause pain and discomfort.
Dermoid Cyst: This cyst type can contain various types of cells, such as hair, teeth, or fatty tissue. Dermoid cysts, which are rare, often develop due to genetic factors.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts usually do not show symptoms and may be discovered incidentally during an ultrasound. However, if noticeable symptoms occur, they may include:
Abdominal Pain and Swelling: Discomfort and pain in the pelvic region, especially with larger cysts.
Menstrual Irregularities: Ovarian cysts can affect the menstrual cycle, leading to irregular or painful menstruation.
Pelvic Pain: Pain in the pelvic region, depending on the size of the cyst.
Causes and Risk Factors
Various factors may contribute to the formation of ovarian cysts:
Genetic Factors: Individuals with a family history of ovarian cysts may have an increased risk.
Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, especially during the menstrual cycle, can contribute to cyst formation.
Endometriosis: The spreading of the inner uterine lining outside the uterus can lead to the development of endometrioma cysts.
Treatment Options
Ovarian cysts often resolve on their own, but if significant symptoms or risk factors are present, treatment may be necessary:
Monitoring and Observation: Small and asymptomatic cysts are typically monitored under a doctor's supervision.
Medication: Drugs aimed at correcting hormonal imbalances can help reduce the size of cysts.
Surgical Intervention: Large or potentially dangerous cysts may be surgically removed.

.jpg&w=100&h=89)

